Beginners Guide to Search Engines

In order to fully get to grips with SEO you need to understand all about search engines, what they are and how they work.
Table of Contents
What are search engines?
A search engine is an online information gathering tool that helps people to find the content, answers and information that they’re looking for. The most common example of a search engine is Google. Whilst there are other popular options such as Bing or Yahoo, when it comes to SEO we tend to focus on Google.
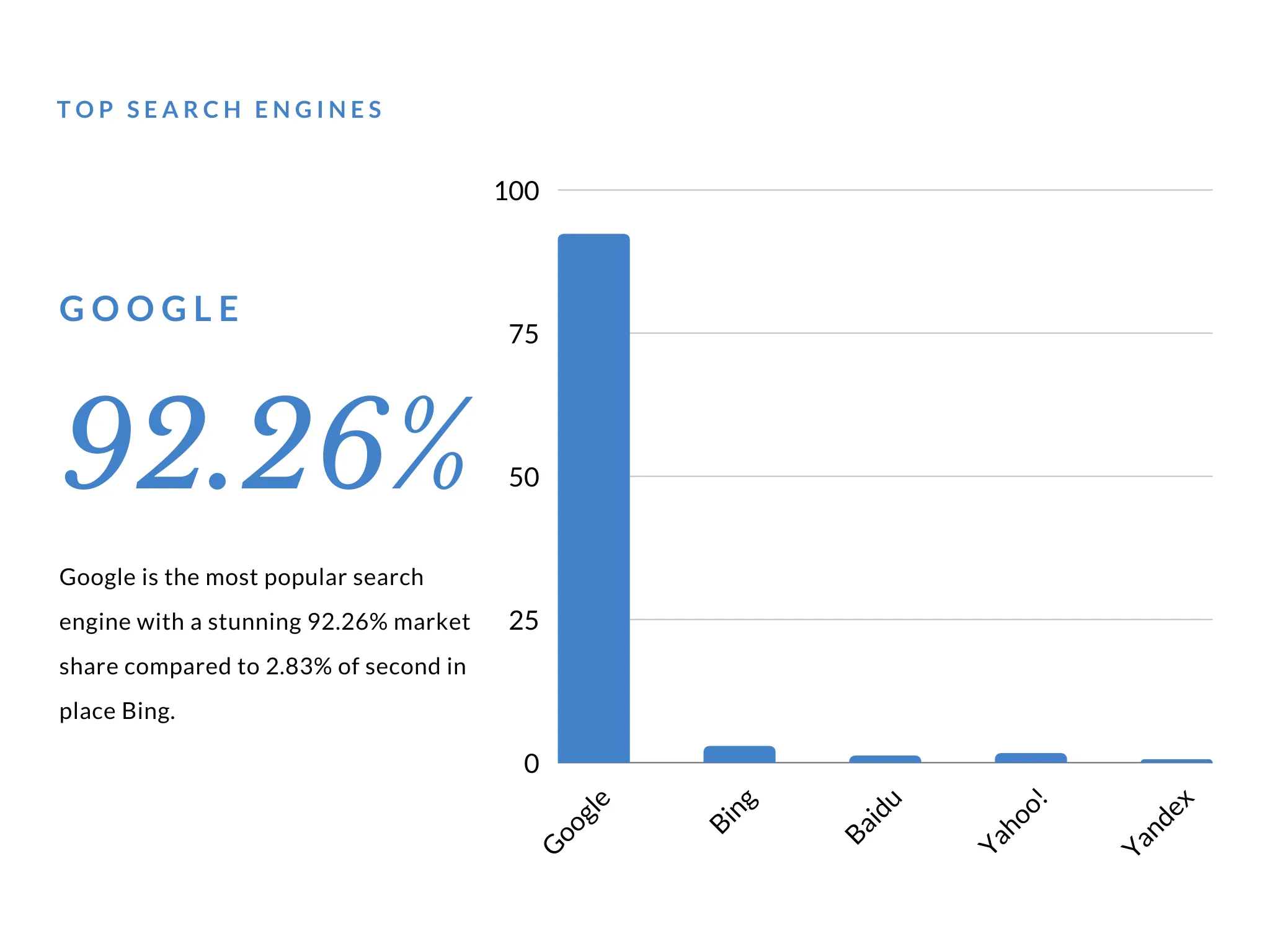
This is because Google is the search engine market leader with a whopping 92% [source] of the market share worldwide. Therefore there’s a good chance that it’s Google your target audience are using to make search queries.
Most search engines work in the same way, so providing your website is optimised for Google, it will likely perform just as well in search rankings for other engines too.
Search engines are designed to search for websites on the internet that provide content that will match a user's search query. They sort through websites within their database and rank the results in order of relevance and quality, giving the user pages of results to choose from.
When search engines work, they follow three key steps:
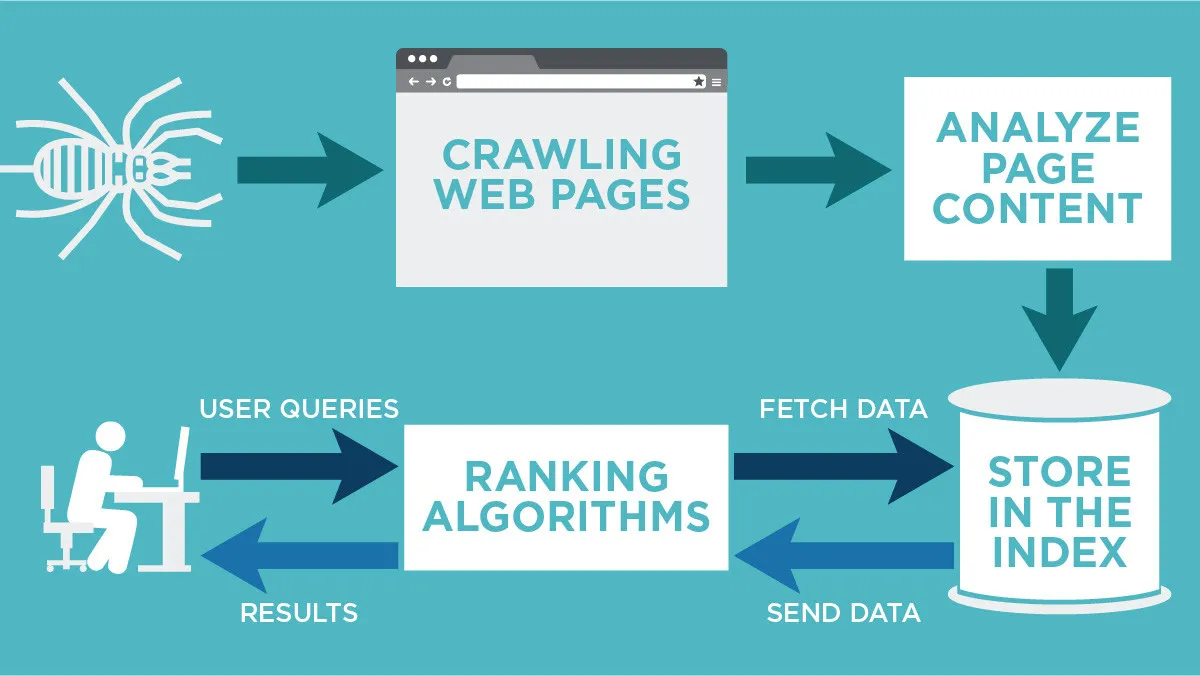
Crawling - The process of search engines looking through web pages on the internet is called crawling. Search engines use crawlers or bots to follow hyperlinks to discover new pages and note any updates to pages they have already found previously.
Indexing - Once the bots have found the webpage, then they index it. Search engines aim to understand the pages and their content, helping them put the web pages into categories. A search engine index is one big store of web pages that can be presented to users once analysed.
Choosing the results - When a user makes a search query, the engine will pull out what it has deemed the best and most relevant web pages for that search term from its index. Users are then presented with a list of results to choose from.
You can use Google Search Console (which we’ll talk about later) to see when your website was last crawled and indexed by Google.
The different types of search
Believe it or not, there are different types of search queries that a user can input into a search engine, and there are things you can do to help you target each one. Google sorts search types into three categories:
- Navigational
- Transactional
- Informational
To ensure that they are providing users with the type of content they’re looking for; search engines need to understand user intent. Search engines don’t just match a search query to a web page that is well optimised for that term; they also read the meaning behind the search to ensure the results are a relevant reflection of what the user is looking for. For example, if Google understands that a user is looking to make a purchase, they will produce a results page featuring online shops instead of blogs or tutorials.
So what do the three search types mean?
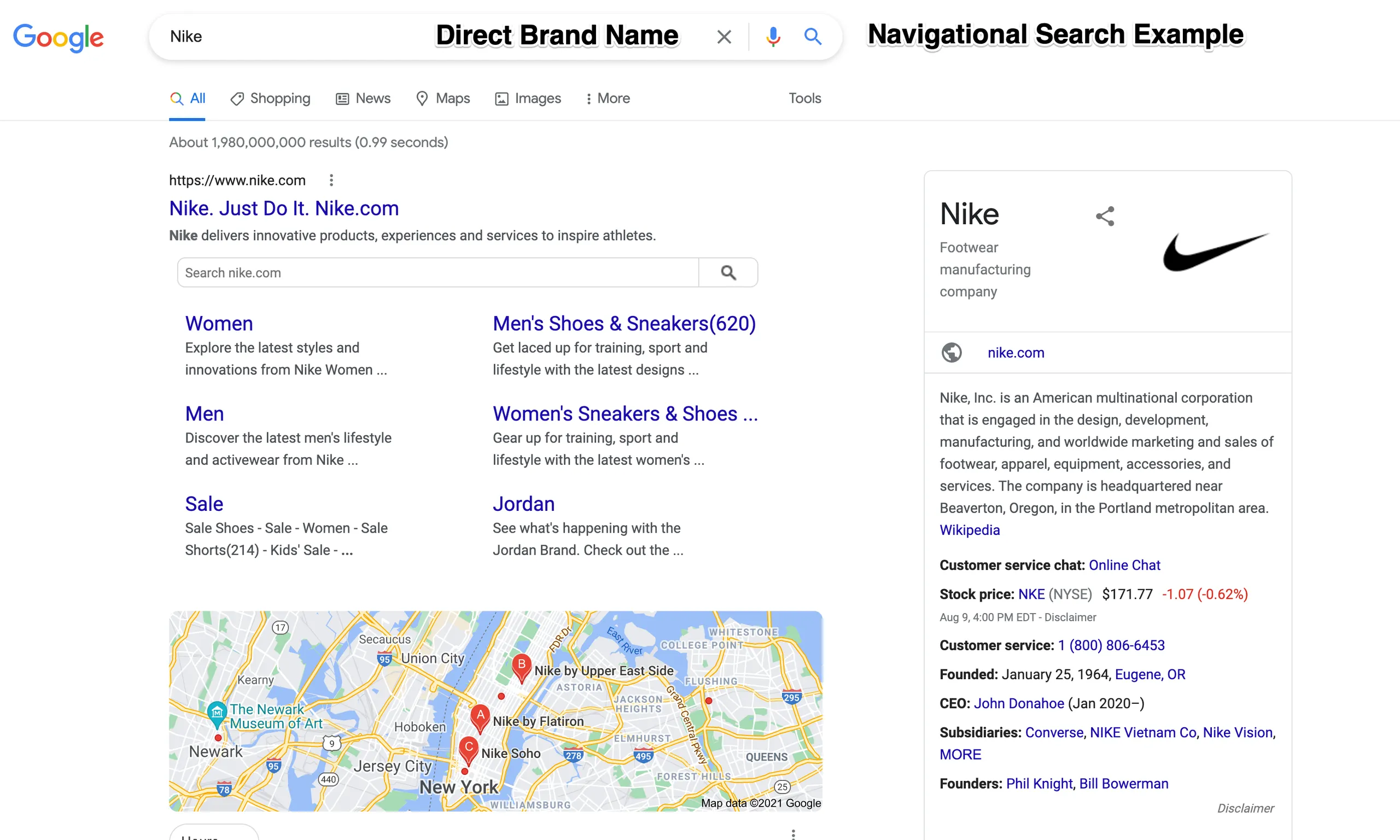
Navigational - A navigational search query establishes that the user intends to visit a specific website or find a particular brand. These search queries have a particular intent behind them; the user knows exactly what result they want Google to give them and where they want to end up. Users type a specific brand name into the search bar and intend to land on that website.
Your website should always appear at the top of results for navigational searches with little work required to get it there (unless you happen to share a brand name with a famous or well-known brand, in which case you’ll face some intense competition for the top spot. If this is the case, it may be worth considering a re-brand…)
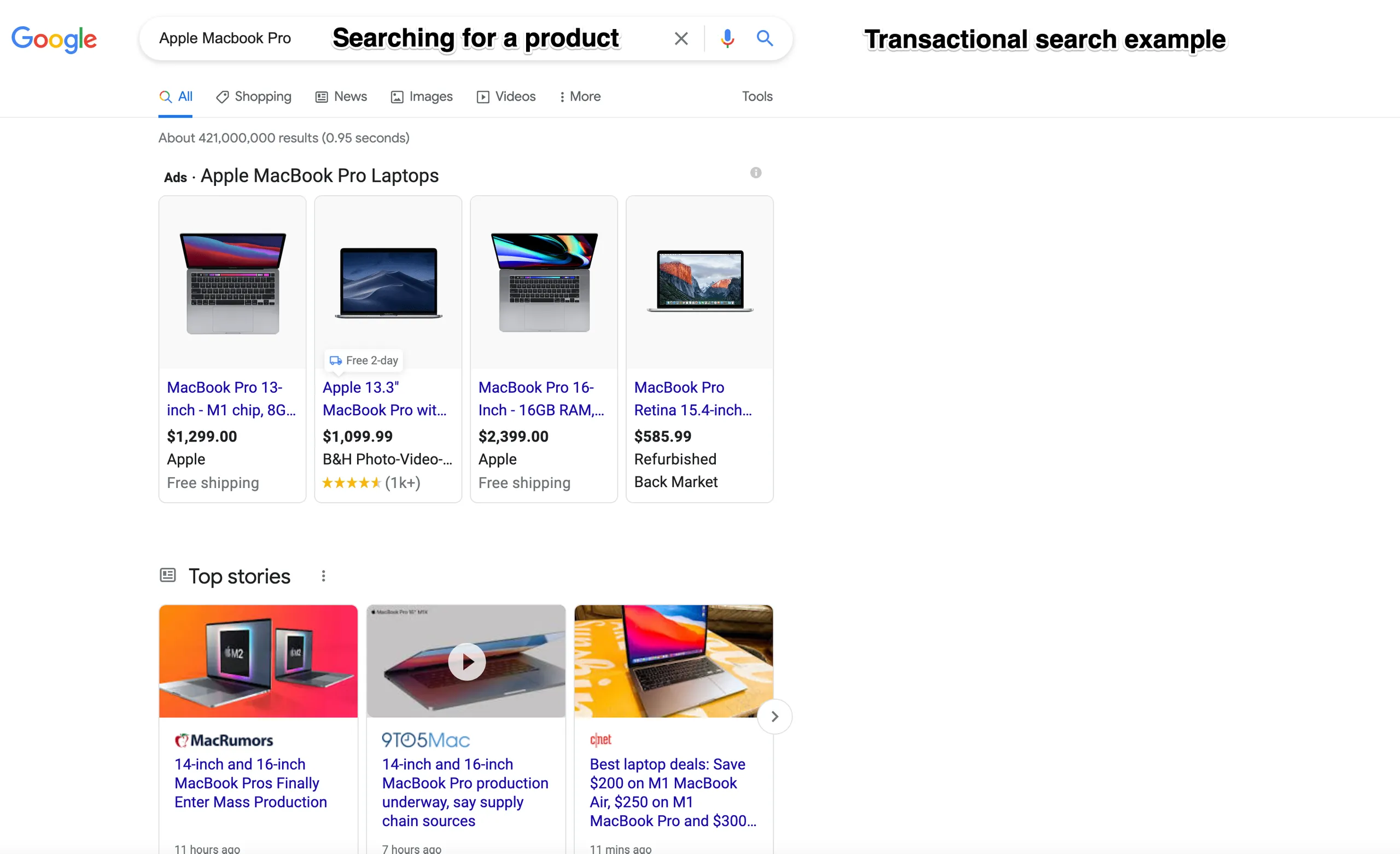
Transactional - A transactional search query is made when a user is looking to make a purchase. They are searching for a product or service that they want to buy. Transactional searches are valuable because users making a transactional search are often much closer to converting than other users. They know they want to make a purchase; they’re just looking for the right place to make it.
Transactional searches can vary in what they feature. For example, sometimes they will feature a specific brand name, e.g. ‘Apple Laptop’, or a more generic ‘lightweight laptop’. Both of these are examples of transactional search queries.
Informational - An informational search query is made when a user looks for information on a specific topic. They may be looking for longer-form content or a tutorial. For example, ‘how to train my dog’ is a search query where the user looks for detailed and high-quality information.
The best way to appear in results for informational search queries is to create high-quality, informative content on your chosen topics. If you want Google to rank your page for these queries, you need to ensure your website contains the information that users are looking for.
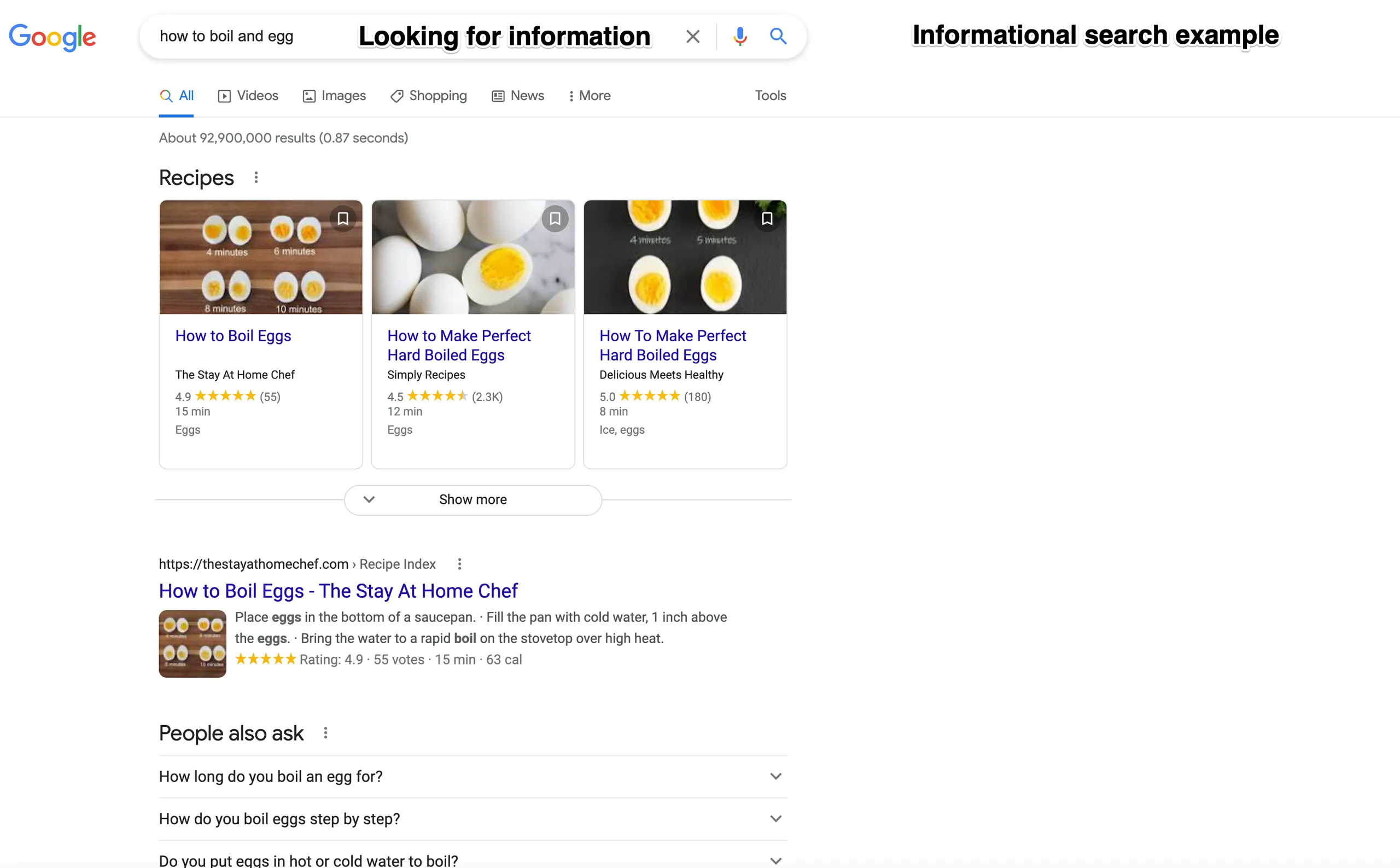
As technology advances, there’s a new type of search in town, voice search. With users able to speak into their watches, mobile phones and smart speakers, search engines are receiving more and more voice searches.
Voice search has prompted search engines to learn how to understand colloquial and more natural phrases. It’s rare for somebody to type the way they speak, and whilst a written search query may say “weather London”, a voice search is more likely to be longer “what is the weather like in London today?”
To successfully optimise for voice search, you first need to understand your audience and how they are searching and behaving online. If you think voice search is a vital part of their online experience, then targeting more conversational keywords and optimising your website for mobile visitors are both essential steps you can take to help your rankings. Check out my guide for optimising for voice search for more information.
Google's Algorithm
The Google algorithm is the formula that Google uses to crawl, rank and present web pages for any given search query. Google employs multiple algorithms to analyse web pages by considering various factors, including quality, relevance and usability.

You'll find more information on some of the key ranking factors that we know for certain makeup part of Google's algorithm below, but the search engine tends to focus on themes such as:
The meaning behind the search - To ensure it's returning the most relevant results possible, Google needs to understand the purpose behind the original search query precisely. They do this by assessing three things:
- The meaning of the words in their native language and context.
- The search intent, what does the user want?
- Is the query time-sensitive? Does it require the most up to date information? E.g.' Weather in London today.
Relevance - Google ensures that the pages it returns in results are relevant to the original search query. It does this by constantly crawling the internet for new or updated web pages. The critical thing that Google is looking for here is keywords that feature both on the web page and within the users search query.
Quality - With millions of web pages out there to choose from, Google needs to make sure it's selecting the very best ones to appear in search results. The algorithm will analyse the quality of a web page by taking into account the level of expertise the content offers and the website's trustworthiness.
User experience - Once Google has assessed a website's content, it will look at the quality of the user experience. Google wants to ensure that any page it presents to a user is user friendly and responsive. Some of the elements it takes into consideration include page speed, navigation and security.
Context - Which search results Google presents to a user is also based on the individual context of the search. The search engine will consider the user's location and search history to ensure the results are exactly what they're looking for.
Google doesn't just rely on its bots and algorithms to rank web pages. They also employ thousands of real-life humans called Search Quality Raters who evaluate the quality of the actual search results for any given search term. While the feedback from these raters doesn't directly impact the rankings of a web page, it does help the search engine fine-tune its algorithms and ensure the systems are working to produce top results.
Here's a short clip from Google showing how real people make Google better:
Google is continuously monitoring and updating its algorithms to ensure they are working to their full potential. The search giants update their algorithms a lot. They make minor tweaks to it multiple times a day. Don’t worry though, these daily changes usually are minimal and not something you’ll notice or that will impact your rankings.
The changes you do need to keep an eye out for are the core updates. Several times a year, Google will make some core updates to its algorithm. Usually, they will announce that these are coming well in advance, giving you plenty of time to ensure your website is optimised for the upcoming changes.
Key Google Ranking Updates to know about
Over the past few years, some key core updates have had a significant impact on how the Google algorithm works and ranks web pages (yes, many of them do have memorable names!)
User Experience Update - June 2021
Link Spam update - July 2021
Panda - The Panda update focused on content and, in particular, aimed to filter out web pages that featured duplicate content and low-quality pages. It also sought to put an end to keyword stuffing, a popular process in the early days of the internet (remember those?!) where web admins would use a high frequency of keywords on a single page to make it rank better.
Rand Fishkin, CEO of Moz.com, talks about the update that first appeared back in 2011:
Penguin - The Penguin update significantly impacted SEO tactics as it focused on links, particularly spammy, low-quality or manipulated backlinks. Many SEO experts had been building extensive backlink profiles to their websites with the help of link farms and buying low-quality links. The Penguin update stopped this as it focused on ranking pages with a natural backlink profile that wasn’t over-optimised.
Hummingbird - The Hummingbird update had one of the most significant impacts on how the algorithm works as it shifted the focus away from keywords and onto user intent. For the first time, Google aimed to understand the search query and the reasons behind it to ensure it was presenting the most relevant results to users.
Pigeon - The Pigeon update got its name thanks to the focus is placed on local search results. The Pigeon update aimed to tie in Google’s local search algorithm more closely with its main web algorithm to improve the relevance and quality of local search results.
Mobile Update - In 2019, Google went ‘mobile-first. This meant that the algorithm would now use the mobile version of a web page in its indexing and ranking. The idea behind it was to reflect better how users were increasingly searching. More than ever, people were and still are using mobile devices to access the internet, and Google wanted to ensure the results it provided were mobile-friendly.
RankBrain - RankBrain is a component of Google’s core algorithm that uses machine learning to determine the most relevant results. Google uses RankBrain as an interpretation model that can apply various possible factors such as location or search history to a query to understand the searchers true intent.
Bert - Google stated that their Bert update was one of the most important updates of recent years. Bert aims to better understand the context of a query by helping Google understand what the words in a search query mean and what context they are being used in. The Bert update was yet another step in Google’s mission to understand the intent behind a search to produce the most relevant results.
Sometimes, you might find your website impacted by one of Google’s core algorithm updates despite doing everything right. If you do, it’s essential to be patient; many of the updates roll out over several days, meaning you may notice constant changes. Wait for everything to settle down before acting.
Google Ranking Factors
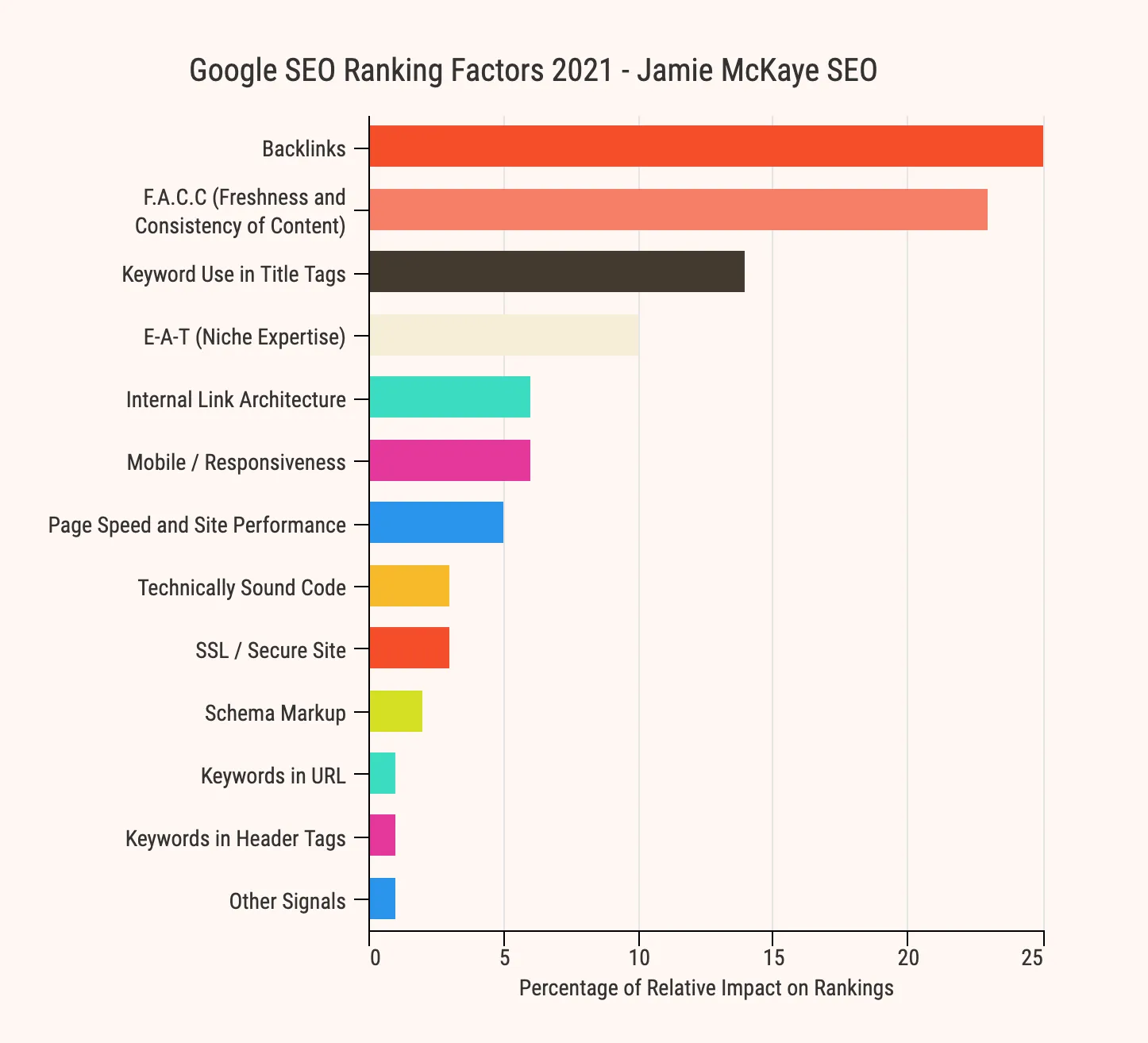
Whilst Google and other search engines haven’t explicitly revealed the calculations and algorithms to rank content, they have given us some guidance. Algorithm updates and announcements have allowed SEO experts to understand what factors Google bots are actively looking for. Below you’ll find some of the ranking factors that Google considers a vital part of its algorithm.
Recommended read: SEO Ranking Factors 2021
High-quality, relevant content - I’ve said it before, and I’ll repeat it, content is king. It doesn’t matter how many technical tweaks you make to your website; Google will never rank your pages without high-quality, relevant content.
Google likes content that’s new and unique. Content that answers users’ questions provides them with the information they were looking for when they made their original search query. One thing Google hates is duplicate content. If the search engine finds duplicate content on your website, it can negatively impact your SEO, so it’s essential to ensure the content you’re creating is original.
Backlinks - Google crawlers will find your website with the help of backlinks. The more links you have pointing to your website, the more reliable Google will deem it to be.
Each link to your website is a signal to Google that someone trusts your content enough to direct users to it. If you can get websites with a high authority to link to yours, then even better. If Google can see that a well-ranking and authoritative website vouches for you, it will give you a great chance of ranking well in search results.
Mobile friendly - In today’s age, more people than ever are using mobile devices to access the internet. Thanks to the way users search and use websites; Google went ‘mobile first’ in 2019. This means that the search engine will now use the mobile version of your website when indexing and ranking it, not the desktop version.
With Google placing such a focus on mobile, it’s crucial that your website is mobile friendly and optimised to function on different mobile devices. If Google thinks the overall experience of your website lacks when accessed on a mobile device, you will face a fall in rankings. Check to see if your site is mobile-friendly here.
Page speed - How fast (or slow) your website loads is another crucial factor for Google. With so many options online, if a user lands on a slow website, chances are they will leave and find a faster alternative, which you don’t want.
Google puts an increased focus on user experience and ensures that users have a positive experience when on your website. This is why page speed is so important. If your website is too slow, Google judges that as a poor user experience and will rank you accordingly. Check out your website performance with Google page speed insights.
User intent - Google matches your content to the intent of the user to rank it appropriately. The search engine wants to understand not just what the user is searching for but why they are making the query.
Google works to understand what type of content the user is looking for when making particular queries to ensure the results they provide are relevant. For your website to rank for specific search terms, you need to ensure that your content matches the original query’s user intent. Please read my article on levelling up your SEO with user intent.
Keyword optimisation - One of the most common SEO tactics is keyword optimisation, and it’s popular for a good reason. When indexing and analysing your website, Google will actively look for keywords and phrases that match the user’s original search query.
Creating keyword-rich content is vital, and there are various ways you can incorporate keywords into your website, including in your title tags, headings, anchor texts and image alt text.
Click-through-rate - Another ranking factor that features in Google’s focus on user experience is click-through-rate. This refers to the number of users who are clicking on your website in search results. The more times your result is selected, the higher Google will rank it as this signals that the result is relevant to the original search query.
You can help to improve your click-through rate by optimising your title tags and meta-descriptions to ensure they’re encouraging users to select your website over other results.
Website security - Way back in 2014, Google announced that it would now consider HTTPS as a ranking factor, meaning website security is a key player when it comes to ranking web pages.
HTTPS encrypts the data between a website and a user’s device and ensures the connection between the two is safe and secure. Google isn’t willing to rank websites that put internet security at risk, so you need to ensure your website is safe and secure and running on HTTPS.
These are just some of the ranking factors that Google uses to index and analyse web pages. It’s unlikely that we’ll ever know the exact formula the search engine uses to rank content, but you’ll notice that almost all ranking factors fall under two categories: quality content and user experience.
Google has advanced from just analysing the content on a page to understanding and determining how a user navigates a website and what their overall online experience is. SEO isn’t just about keywords and backlinks; although these are two essential factors, you should be focusing on how your web page meets the needs of users both in terms of the information and the quality of the experience you provide them.
We’ll cover all of the above in more detail further on in the guide, too, so you can ensure you’re optimising your website with Google’s key ranking factors in mind.



Comments